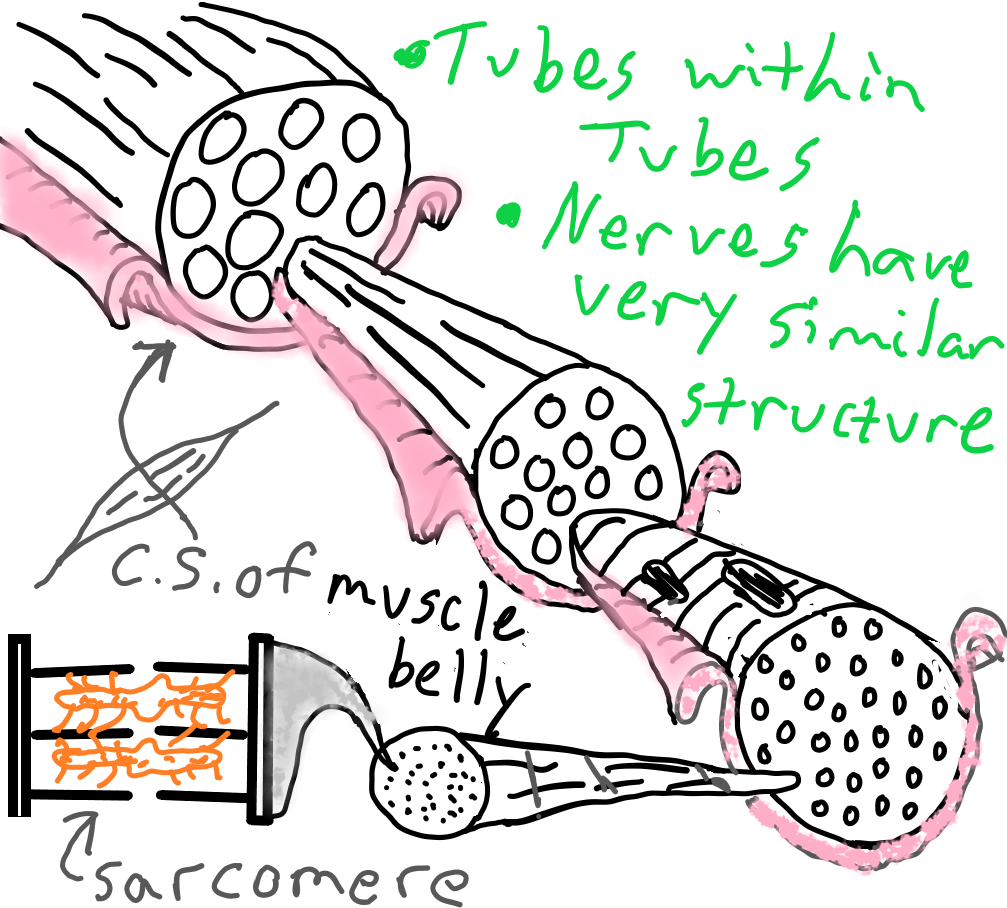
Skeletal muscle’s function is to contract and cause movement. This figure represents the different levels of muscle organization. This 3-D anatomy is difficult to remember and keep straight in your brain. It also may be rather difficult to visualize this figure in your mind. You will be very glad if you can, though, as it is an important Anatomy & Physiology topic. Realize that the levels of organization of a nerve are very similar to this muscle organization, even using very similar terminology (word anatomy: neuro- instead of myo-).
A key point of reference to remember is that muscle cell ~ muscle fiber. Muscle cells end-to-end form a muscle fiber. There are then higher and lower levels of organization from this point. For example, a bundle of these muscle fibers is called a muscle fascicle. And going smaller, a muscle cell, or myocyte, contains many myofibrils. The myofibrils are each composed of sarcomeres (basic functional unit of muscle) aligned end-to-end. I hope this helps you get a good start into learning about muscle anatomy, which is closely tied to muscle physiology (how a muscle actually works or functions).